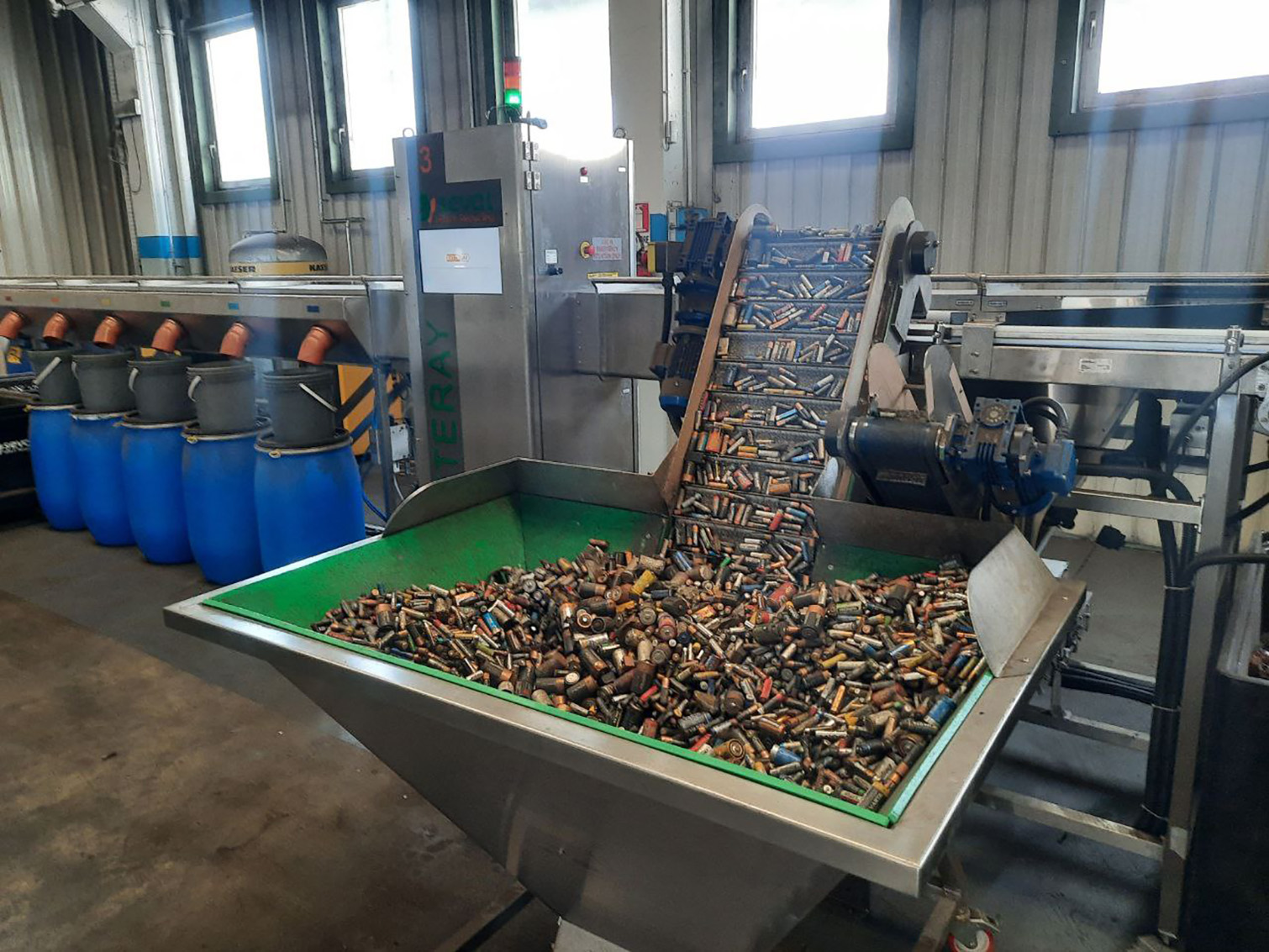
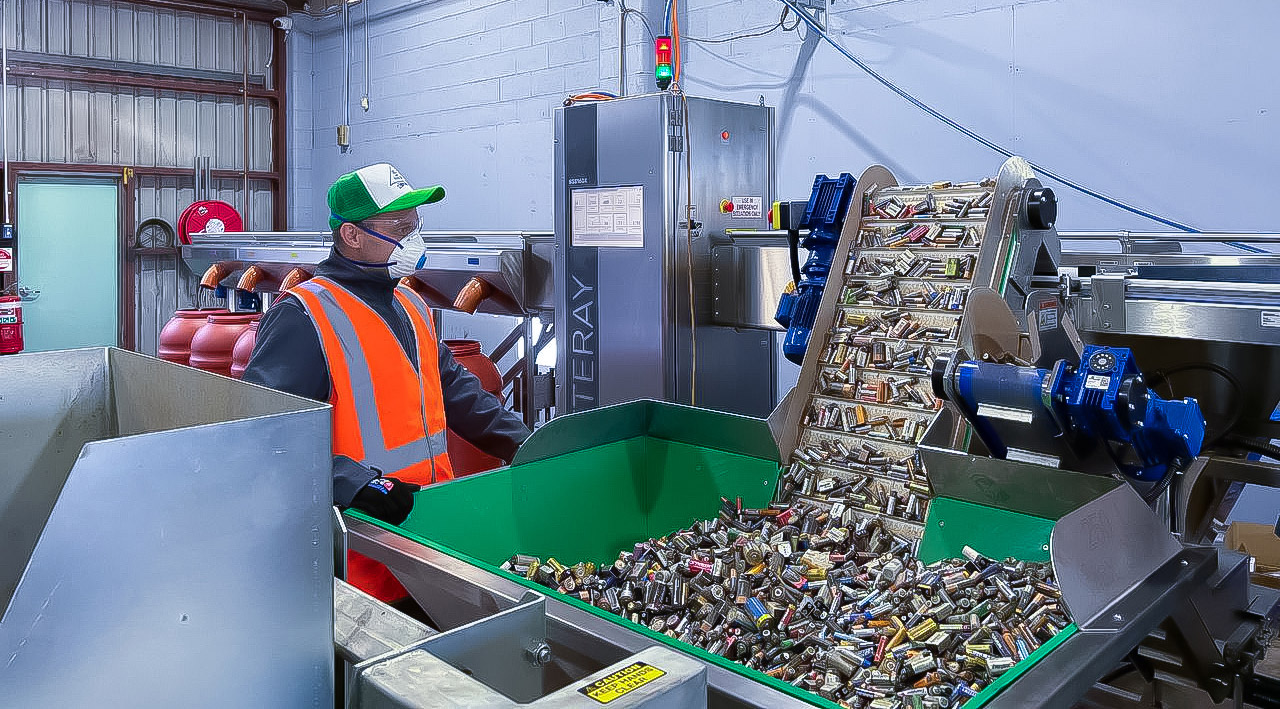
The bulk of batteries arriving at recycling plants come from ordinary inhabitants of our planet. Typically, these are small to medium-sized consumer electronic devices, the lifespan of which is sometimes comparable to the charge level of the battery inside.
These batteries vary in size and chemical composition. Currently in circulation are: Alkaline, zinc (Zn), nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), nickel-cadmium (NiCd), non-rechargeable (Primary-Li), and rechargeable lithium (Li-Ion). The most common household battery types are alkaline (AA, AAA, C, D, 9V), lithium, zinc, and nickel-metal hydride.
Alkaline batteries are used in many everyday devices, such as TV remotes, toys, calculators, radios, wireless mice and keyboards, and medical thermometers and blood pressure monitors. Compared to the cheaper and more common alkaline type, lithium batteries boast a longer run time and are used in more demanding devices such as video cameras, car keys, and remote controls.
Zinc batteries, such as hydrocarbon and zinc-carbon, are usually cheaper and are used in low-power consumption devices such as household scales, flashlights, and watches.
Nickel-cadmium batteries have several advantages: low self-discharge, fast charging, and high resistance to cyclic charging and discharging. They were widely used in the past in various devices, but their popularity has declined due to the development of more modern technologies such as nickel-metal hydride and lithium-ion batteries, which have a higher capacity and less “memory” effect. However, nickel-cadmium batteries are still used in some specialized applications, such as aviation and communications equipment.
Nickel-metal hydride batteries are often used in rechargeable devices such as portable electronic devices (e.g., cameras, camcorders), power tools, and toys, as well as in hybrid and electric vehicles. They are also widely used in energy storage applications such as alternative energy sources and backup power systems. NiMH batteries can be used over a wide temperature range and have a long service life, making them a popular choice for various industrial and commercial applications where reliable and efficient power is required.
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in many fields due to their high energy densities, reliability, and long service life. Some of their main applications include portable electronic devices (smartphones, laptops, tablets, cameras), electric vehicles (EVs and hybrid vehicles), supplementary energy sources (energy storage for homes, commercial buildings, and solar farms), and aviation and space (unmanned aircraft and spacecraft).
The X-ray system for sorting of portable waste batteries and accumulators BATTERAY allows us to sort all the chemical types of batteries described above. The battery format can be any cylindrical shape. The use of an AI algorithm enables us to ensure not only high purity of the sorted fraction but also achieve productivity several orders of magnitude superior to manual sorting methods.